
Squatter's Rights (1946)
possession against the Crown (commonly known as "squatters rights"). A comprehensive review of the Act and its service delivery model is required to ensure it is still relevant and is the most effective way to manage, administer, utilize and protect our Crown lands for the people of Newfoundland and Labrador.

Squatter's Rights Laws and Tips for all 50 States eForms Learn
Dakota. In South Dakota, as outlined in S.D. Codified Laws Ann. § § 15-3-1, 15-3-15, a squatter must meet the general requirements for adverse possession and occupy the premises for 20 years to claim adverse possession/color of title. For payment of taxes, the requirement is 10 years.

What are Squatters Rights? Why Do Squatters Have Rights?
Squatters rights, or adverse possession laws, govern how landlords and property owners can remove trespassers after they've established residency. Squatters rights vary by state law. Trespassers can become squatters if they stay long enough and live in the property overtly. They must be evicted, rather than immediately ejected by police.

What Are Squatters Rights? StatebyState Guide to Squatters Rights
Squatter's rights, also known as adverse possession, is a legal principle in the Anglo-American common law system that allows individuals without legal title to a property to potentially acquire legal ownership based on continuous possession or occupation without the permission of the property's legal owner. This concept may seem surprising to some, but it has been a longstanding element of.

An Inside Look at Squatter's Rights
If someone can find an Act or Law showing me that a squater has the rights to encroach on and claim private land in Newfoundland Ca. yes please continue. If someone can find an Act or Law showing me if a squatter has or has not the rights to encroach on and claim my privately owned property that would be great.

What are squatters rights and how do they work? Find out now
January 9, 2023 The Provincial Government is seeking public and stakeholder input on amendments to section 36 of the Lands Act. This section focuses on adverse possession of Crown lands - commonly referred to as "squatters' rights."
What are Squatter Rights Landlord FAQs TurboTenant
The current law in Newfoundland and Labrador cuts off squatter's rights against the Crown as of Jan. 1, 1977, with the only exception being that people can keep land they occupied for the 20 years before the law changed. French said courts have ruled that it's only the period right before the law changed, from Dec. 31, 1956 to Dec. 31, 1976..

Squatter's Rights Laws and Tips for all 50 States eForms Learn
Criminal Proceedings Under the New Law To end this great injustice, they invented the following: If a public prosecutor wants to have a squat evicted, he submits a request to a Judge Commissioner (Rechter Commissaris, or RC). The RC must make a decision within three days whether this request is well-founded and whether evacuation is allowed.

Squatters Rights YouTube
The provincial government abolished squatter's rights in 1976, instead requiring property owners to have a Crown grant if they believe they own land that was once public. Alternatively,.

Why Do Squatters Rights Exist? How Money Works YouTube
Page 5 of 58 REFORMING THE LAW ON ADVERSE POSSESSION Several statutory instruments affect land titles and conveyancing in the Province of Newfoundland and Labrador, one of the foremost of which is the Lands Act, S.N.L. 1991, c. 36. Section 36 of the Lands Act addresses the issue of adverse possession of land as against the Crown's interest.

What You Need to Know About Squatter Rights and Evictions
You're into an adverse possession claim ("squatters' rights") against the house and land. There are two types of squatters' rights: against the Crown (the 20 year period from Dec. 31, 1956 to Jan. 1st, 1977), and as against any private interest (10 years back from the date you begin adverse possession). Small municipalities can seize and sell.

What landlords need to know about squatters rights in 2022
Squatting in the Netherlands ( Dutch: kraken) is the occupation of unused or derelict buildings or land without the permission of the owner. The modern squatters movement ( Dutch: kraakbeweging) began in the 1960s in the Netherlands.

Squatter's Rights (1946) Official HD Trailer
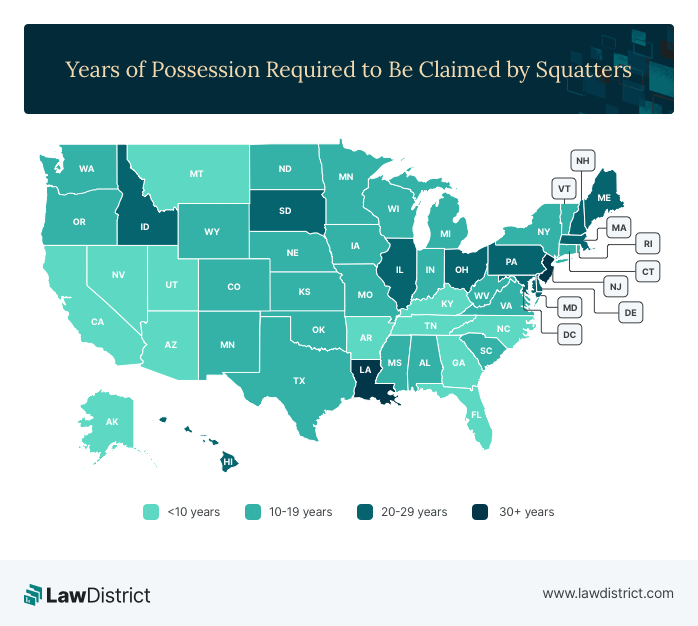
Squatters' rights, or Adverse Possession, refer to the rights a squatter may gain if they occupy a property for a certain period without the owner taking legal action against them. The time frame for establishing squatters' rights varies by state, ranging from 7 years to over 20 years.

What are Squatter Rights Landlord FAQs TurboTenant
The present legislation in Newfoundland and Labrador cuts off squatter's rights towards the Crown as of Jan. 1, 1977, with the one exception being that individuals can preserve land they occupied for the 20 years earlier than the legislation modified. French mentioned courts have dominated that it's solely the interval proper earlier than.
Squatter Rights in 2024 What a Property Owner Needs to Know
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building, usually residential, that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there were one billion slum residents and squatters globally.

Squatter's Rights (1946) YouTube
The Dutch squatting ban refers to the law (Dutch: Wet Kraken en Leegstand) introduced on 1 October 2010, under which squatting in the Netherlands became de jure illegal. Criminalization had first been proposed in the 1970s, but was opposed by the Council of Churches. In 2006, a new plan was proposed and backed by parties including VVD and PVV.When the new law was introduced, squatters occupied.