
Image result for oxidative and substrate level phosphorylation School study tips, Biochemistry
In these steps, a phosphate group is transferred from a pathway intermediate straight to ADP, a process known as substrate-level phosphorylation. Many more steps, however, produce ATP in an indirect way. In these steps, electrons from glucose are transferred to small molecules known as electron carriers.
.PNG)
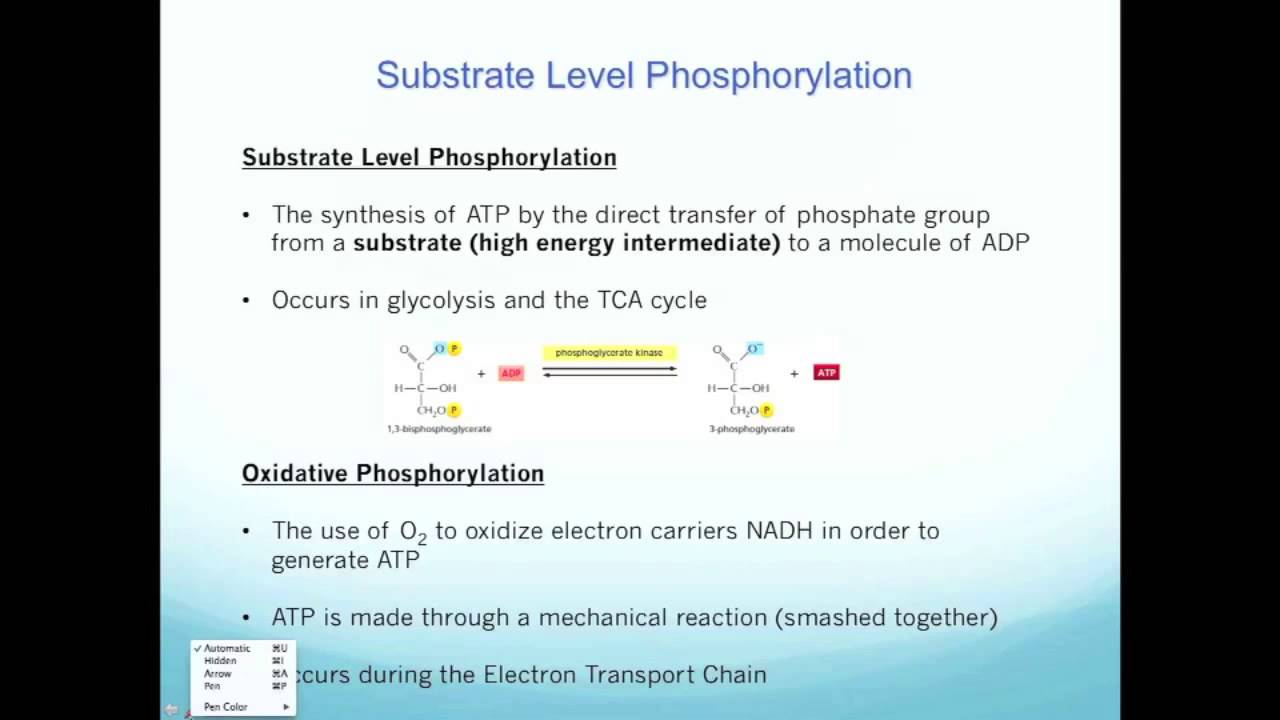
SubstrateLevel Phosphorylation
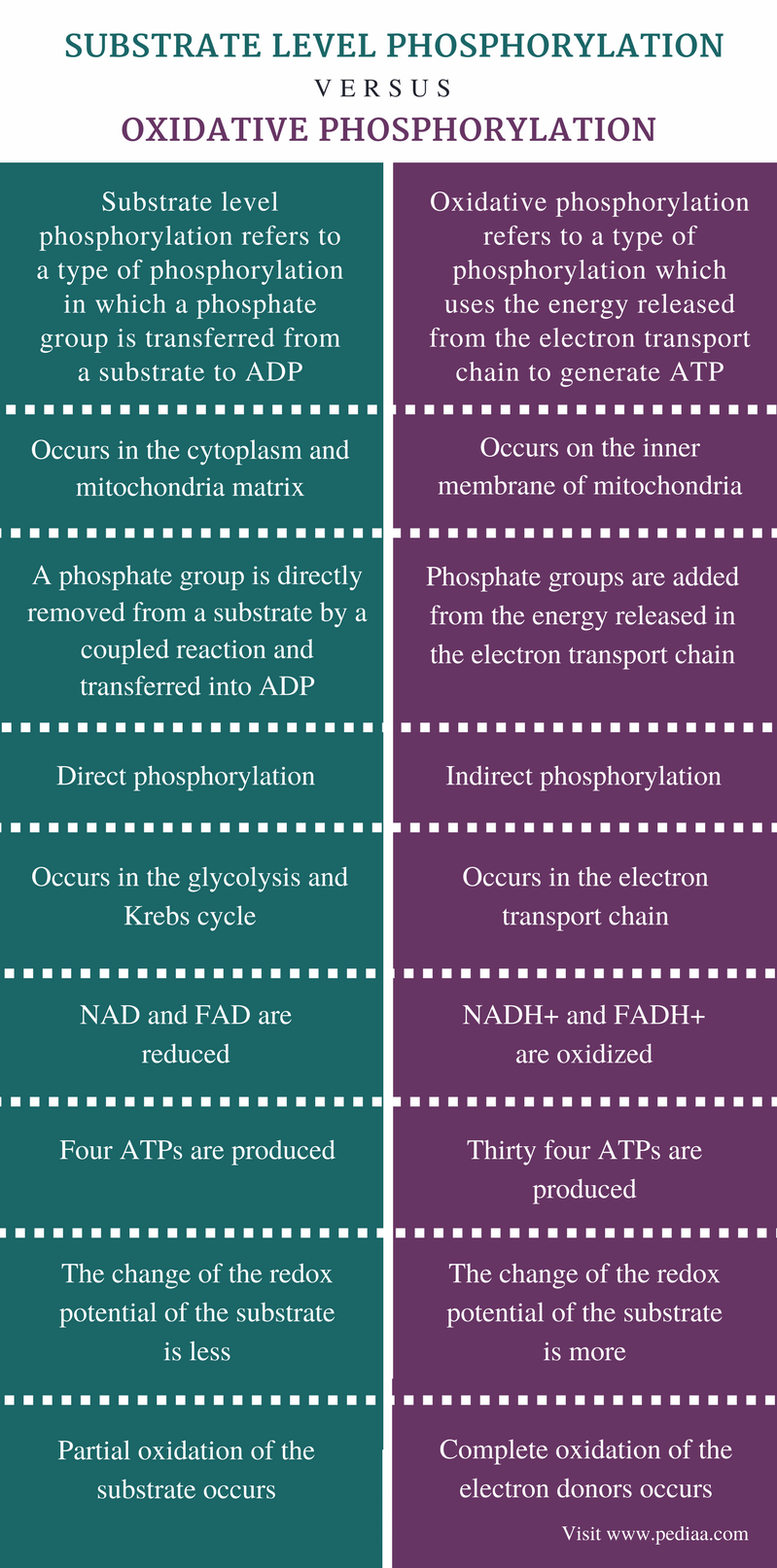
Substrate level phosphorylation refers to a type of phosphorylation in which a phosphate group is transferred from a substrate to ADP. It can also add a phosphate group to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) in order to form a guanosine triphosphate (GTP).

Phosphorylation Basics
The steps by which new ATP is created has the name of substrate-level phosphorylation. Investment Phase. In this phase, there are two phosphates added to glucose. Glycolysis begins with hexokinase phosphorylating glucose into glucose-6 phosphate (G6P). This step is the first transfer of a phosphate group and where the consumption of the first.

How Many Substrate Level Phosphorylation In Krebs Cycle Wasfa Blog
True. Substrate level phosphorylation (physical addition of phosphate to the ADP and building ATP) can happen during glycolysis and TCA in the matrix of mitochondria. This paper contrasts substrate phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation:

Image result for oxidative and substrate level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation
And then we have again, five ATP and two ATP here, forming substrate level phosphorylation is two ATP. And six NADH times two point five is going to yield 15. And two FADH two times one point five is going to yield three. And so, if we add all of this up, we get 32 ATP.
Substrate level vs. Oxidative Phosphorylation YouTube
This very direct method of phosphorylation is called substrate-level phosphorylation. Oxidative Phosphorylation. Most of the ATP generated during glucose catabolism, however, is derived from a much more complex process, chemiosmosis, which takes place in mitochondria (Figure 3) within a eukaryotic cell or the plasma membrane of a prokaryotic.
Substratelevel Phosphorylation Definition, Example, & Importance
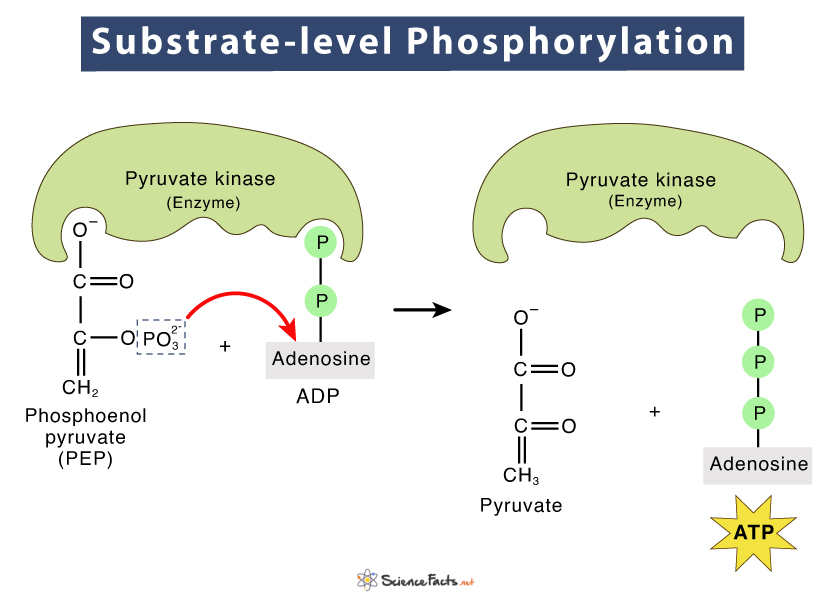
Substrate-level phosphorylation is an exergonic reaction that is responsible for the transfer of a phosphoryl group from a substrate to a nucleoside diphosphate (ADP or GDP) to form a.
Difference between Substrate level phosphorylation, Oxidative phosphorylation and
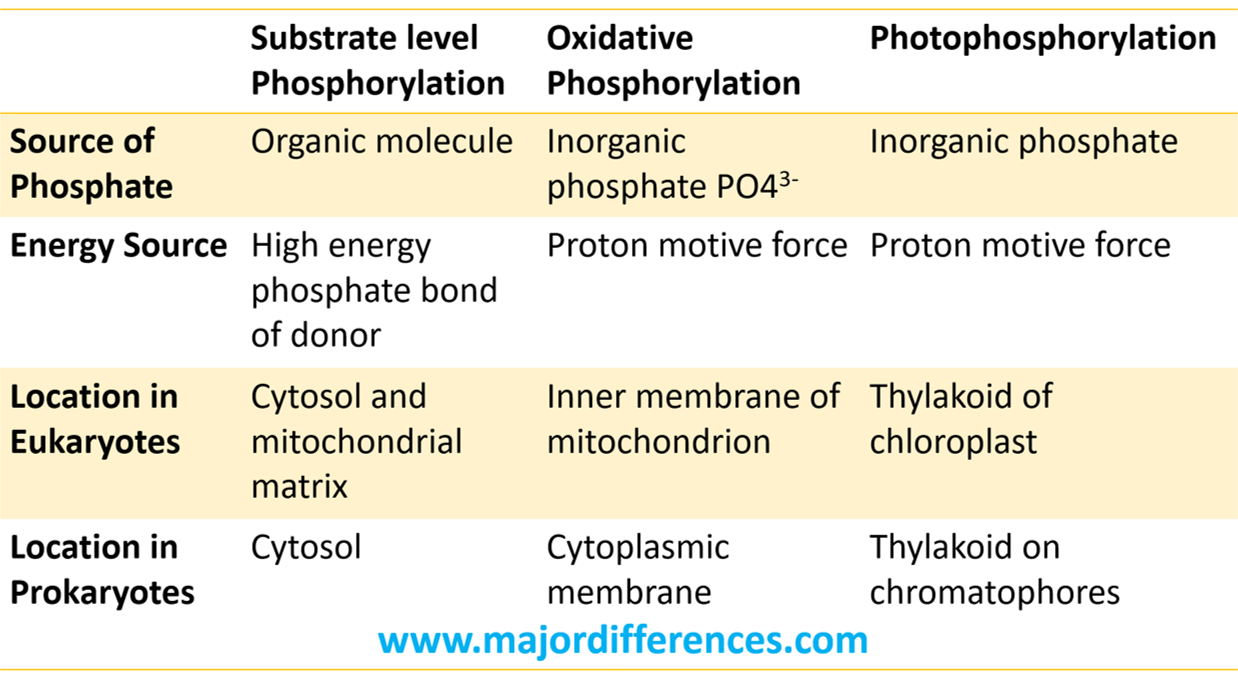
Substrate-level phosphorylation is one of the ways in which a phosphate group is introduced into a molecule. Another is oxidative phosphorylation. In substrate-level phosphorylation, the PO 43- from a phosphorylated substrate is transferred to ADP to form ATP. Phosphorylases and kinases catalyse this process.
PPT Cellular respiration Part 2 Kreb Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2405145
Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs twice in glycolysis and once in the TCA cycle. The "purpose" of fermentation. The oxidation of a variety of small organic compounds is a process that is utilized by many organisms to garner energy for cellular maintenance and growth. The oxidation of glucose via glycolysis is one such pathway.

Substrate Level Phosphorylation vs Oxidative Phosphorylation neetpg nextpg YouTube
Overall, the theoretical maximum yield of ATP made during the complete aerobic respiration of glucose is 38 molecules, with four being made by substrate-level phosphorylation and 34 being made by oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 8.16). In reality, the total ATP yield is usually less, ranging from one to 34 ATP molecules, depending on whether.

How Many Substrate Level Phosphorylation In Krebs Cycle Wasfa Blog
In substrate-level phosphorylation a phosphoryl group is transferred from an energy-rich donor (e.g., 1,3-diphosphoglycerate) to ADP to yield a molecule of ATP. This type of ATP synthesis (reactions [7], [10], and [43]) does not require molecular oxygen (O 2 ), although it is frequently, but… Home Science Chemistry Science & Tech phosphorylation
Difference Between Substrate Level Phosphorylation and Oxidative Phosphorylation
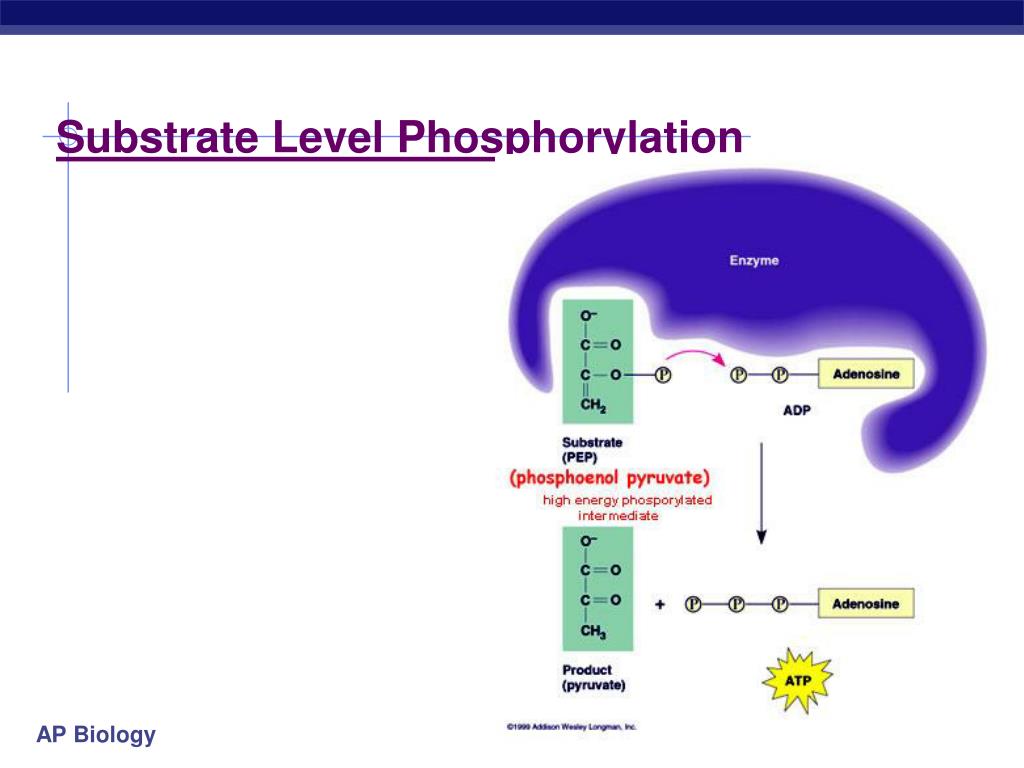
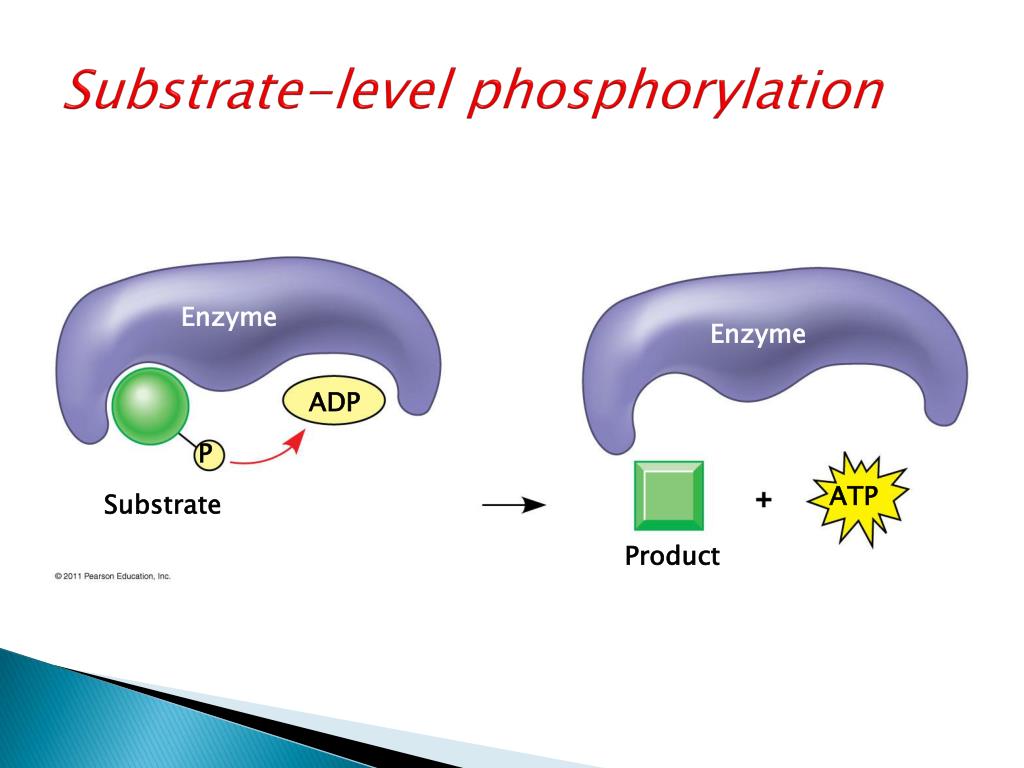
Substrate Level Phosphorylation. The easiest type of phosphorylation to understand is that which occurs at the substrate level. This type of phosphorylation involves the direct synthesis of ATP from ADP and a reactive intermediate, typically a high energy phosphate-containing molecule. Substrate level phosphorylation is a relatively minor.
[Solved] What are the comparisons of oxidative phosphorylation,... Course Hero
Overview of oxidative phosphorylation. The electron transport chain forms a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which drives the synthesis of ATP via chemiosmosis. Why do we need oxygen? You, like many other organisms, need oxygen to live.
PPT Chapter 9 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2823222
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation. Substrate-level phosphorylation is the production of ATP from ADP by a direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from a phosphorylated intermediate metabolic compound in an exergonic catabolic pathway as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). Such intermediate compounds are sometimes called high-energy.

Substrate Level Phosphorylation A Process That Occurs In The Absence Of Light
Substrate level phosphorylation. The direct formation of ATP from ADP is linked to the hydrolysis of certain phosphorylated intermediates of the catabolic pathways.
.PNG)
SubstrateLevel Phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP supported by the energy released from another high-energy bond that leads to phosphorylation of ADP or GDP to ATP or GTP (note that the reaction catalyzed by creatine kinase is not considered as "substrate-level phosphorylation").